When using tcpdump, you often need to tell it which network interface to capture packets from. A computer might have multiple interfaces (like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or virtual adapters), and choosing the right one is important for accurate packet capture.
If you don’t specify an interface, tcpdump will usually pick one by default — but it might not be the one you want.
Finding Available Interfaces
You can list all available interfaces using this command:
tcpdump -DThis will output something like:
1.eth0
2.wlan0
3.lo

Each line shows the interface number and name.
Using a Specific Interface
To start capturing on a specific interface, use the -i option followed by the interface name:
tcpdump -i wlan0This tells tcpdump to listen on the wireless interface.
You can also use the number from tcpdump -D, like:
tcpdump -i 2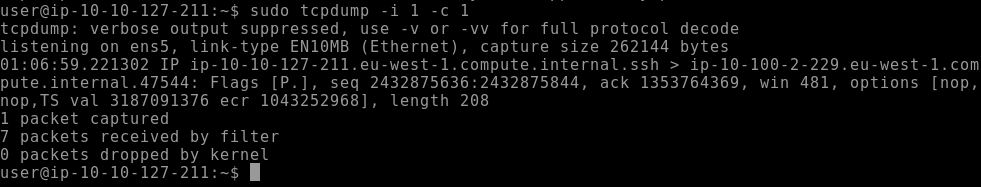
Common Interface Names (Linux)
| Interface | Purpose |
|---|---|
| eth0 | Wired Ethernet |
| wlan0 | Wireless (Wi-Fi) |
| lo | Loopback |
| enp3s0 | Wired (modern name) |
| wlp2s0 | Wireless (modern name) |
Names may vary depending on the system.
