Windows Firewall is a security feature built into the Windows operating system. It controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules to protect the computer from unauthorized access or malicious threats.
Purpose of Windows Firewall
The primary goal of Windows Firewall is to protect the system from network-based attacks by controlling the flow of data to and from the computer.
- Blocks or allows traffic based on security policies.
- Helps prevent unauthorized access to the system.
- Monitors network connections for potential threats.
How Windows Firewall Works
Windows Firewall works by analyzing network traffic and applying rules to decide whether the traffic is allowed or blocked.
- Inbound traffic: Requests or data coming into the system are checked.
- Outbound traffic: Data leaving the system is also monitored.
- Rules: Specific rules are created for apps, services, and network addresses to permit or deny access.
Key Features of Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall offers several important features that help secure a computer.
- Customizable rules: Users can create specific rules for applications or network addresses.
- Profile-based configuration: Different firewall settings can be applied for home, work, or public networks.
- Monitoring: Logs and alerts help administrators monitor firewall activity.
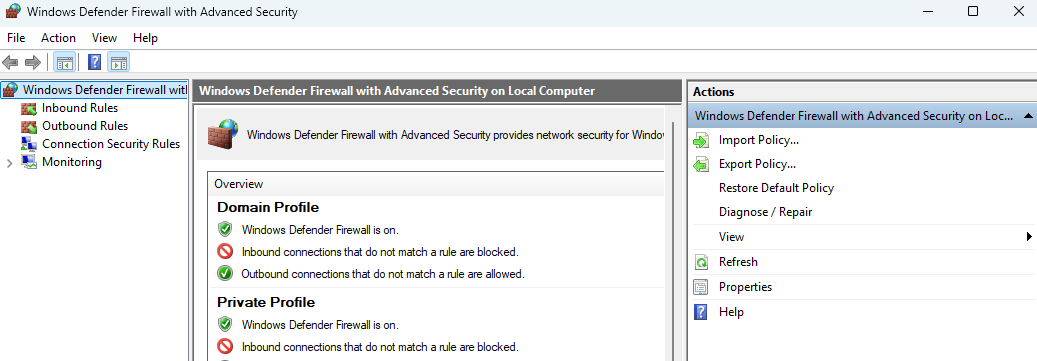
Firewall Profiles
Windows Firewall uses different profiles to control traffic based on the type of network the system is connected to.
| Profile | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain Profile | Used when the system is connected to a corporate network. |
| Private Profile | Applied when connected to a trusted home or office network. |
| Public Profile | Used when connected to a public network like a cafe or airport. |
Configuring Windows Firewall
You can configure Windows Firewall settings through the Control Panel or the Windows Settings app.
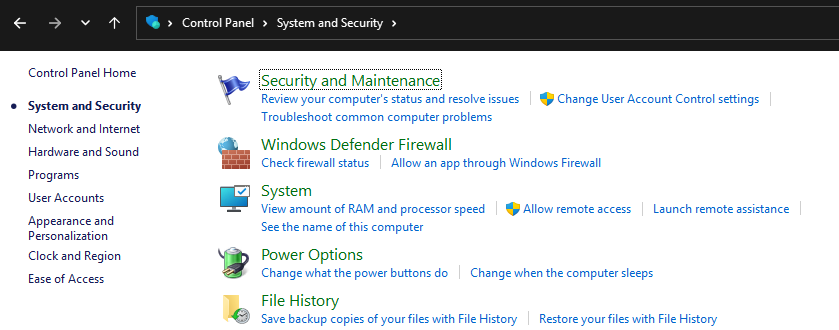
- Control Panel: Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall.
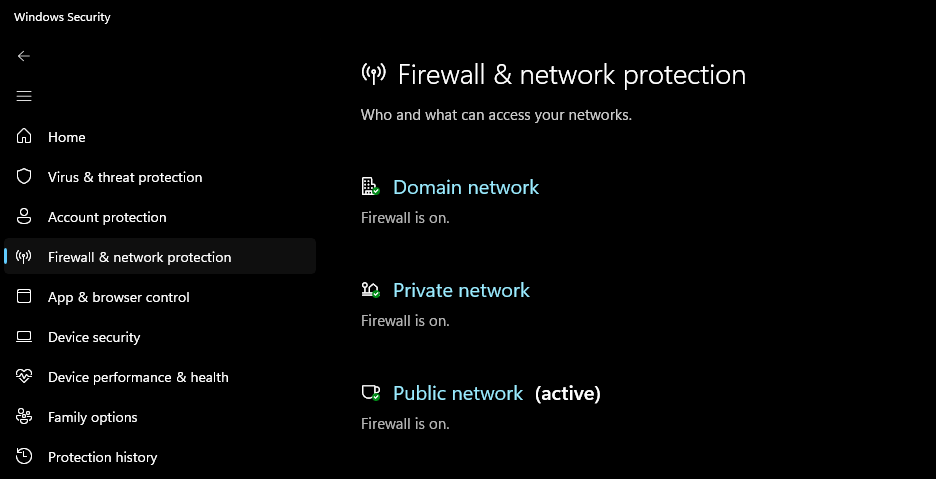
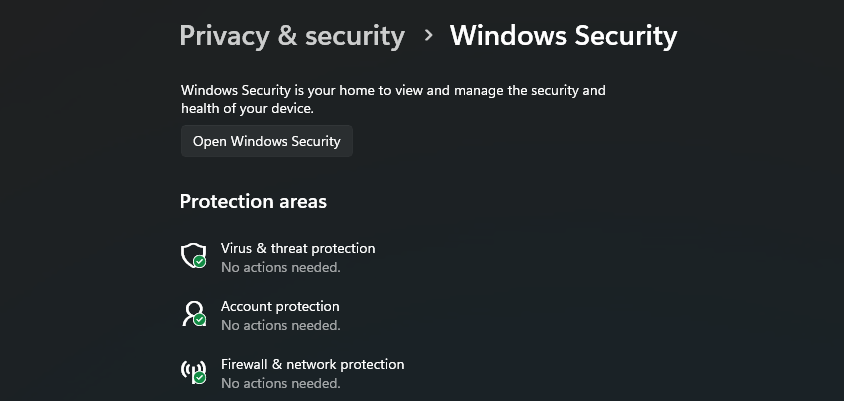
- Windows Settings: Open Settings > Privacy & Security > Windows Security > Firewall & Network Protection.
Advanced Features
Advanced users can take advantage of additional configuration options.
- Advanced Security: Allows fine-grained control over inbound and outbound rules.
- Command line: The
netshcommand can be used for managing firewall settings through a command prompt.
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state on
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Allow MyApp" dir=in action=allow program="C:\Path\To\MyApp.exe"